Here comes another edition of my newsletter. This month I was away from the computer for a whole week, but I’ve collected some interesting resources on AI and LLM security – most of them published in the first two weeks of September.

Thumbnail generated with Stable Diffusion 🙂
LLM Security
Dropbox LLM Security
This repository contains scripts and descriptions that demonstrate attacks on LLMs using repeated characters. Long story short: if you supply a long string of a single character (or sequence of characters), the model will hallucinate. Also, it may reveal its instructions.

Link: https://github.com/dropbox/llm-security
LLM apps: Don’t Get Stuck in an Infinite Loop!
Post by @wunderwuzzi about looping ChatGPT through Indirect Prompt Injection. I am not sure if that can be classified as a DoS attack, but if you’d classify it as such, then it’d probably be the first publicly demonstrated DoS on LLM!
Link: https://embracethered.com/blog/posts/2023/llm-cost-and-dos-threat/
BlindLlama by Mithril Security
BlindLlama by Mithril Security is a project that provides “zero-trust AI APIs for easy and private consumption of open-source LLMs”. In other words, if you were concerned about passing confidential data to the LLM’s API and at the same time you didn’t want to deploy open-source models locally, this might be the solution for you.
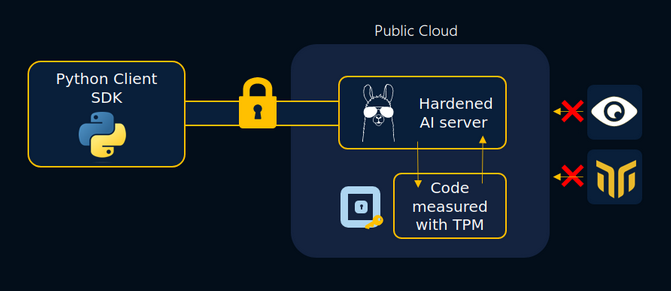
Links: blog: https://blog.mithrilsecurity.io/introducing-blindllama-zero-trust-ai-apis-with-privacy-guarantees-traceability/ + docs: https://blindllama.mithrilsecurity.io/en/latest/ + Github: https://github.com/mithril-security/blind_llama/
Demystifying RCE Vulnerabilities in LLM-Integrated Apps
According to the authors, these two factors have a huge impact on the security of LLM-integrated applications:
- the unpredictable responses of LLMs, which can be manipulated by attackers to bypass developer restrictions (using specific prompts)
- the execution of untrusted code generated by LLMs, often without appropriate checks, allowing remote code execution.
This has serious implications not only for LLMs, but also for applications integrated with LLMs.
Authors proposed automated approach for identifying RCE vulnerabilities in LLMs – LLMSmith:
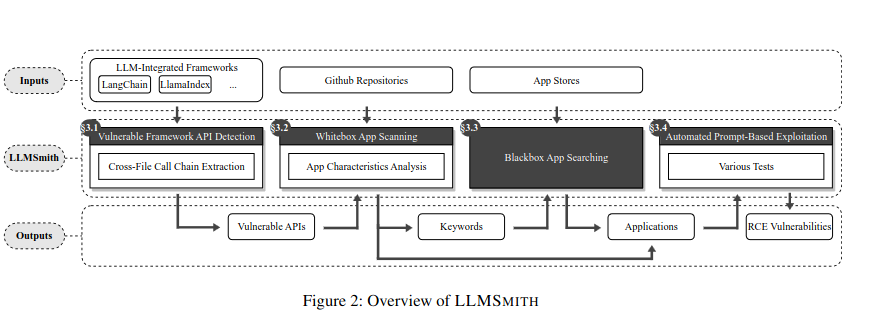
According to the article, they have created “the first automated prompt-based exploitation method for LLM-integrated apps.”, unfortunately, I could not find LLMSmith’s source anywhere…
Link: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2309.02926.pdf
AI Security
Some more resources from DEFCON31
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=W8fbKYjbFD4
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=k9gt7MNXPDY
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QWaW23sraZ8
38TB of data accidentally exposed by Microsoft AI researchers
Wiz Research found a data exposure incident on Microsoft’s AI GitHub repository.
MLSecOps Podcast: Rob van der Veer and Ian Swanson
AI veteran Rob van der Veer in MLSecOps podcast. One of the topics discussed by the speakers is ISO 5338, a new standard for AI system life cycle processes
AI/LLM as a tool for cybersecurity
LLM in the Shell: Generative Honeypots
In this paper, authors demonstrated an interesting application of LLMs – they’ve used them as a honeypot backend in the sheLLM project. An idea is to trick an attacker into thinking that he’s using a real shell, meanwhile the outputs for given shell commands are generated by the LLM. It makes me wonder though – what would happen if an attacker realizes that he’s using LLM? Prompt Injection through this shell could be pricey for owners of the honeypot!
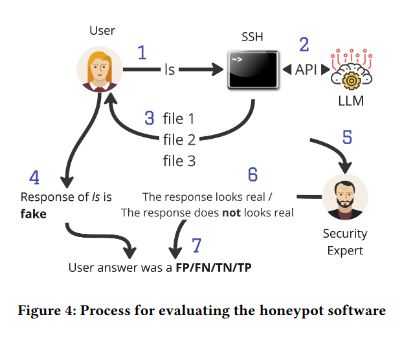
Link: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2309.00155.pdf
Automatic Scam-Baiting Using ChatGPT
That’s a brilliant idea for the usage of LLM – baiting scammers, making them lose money and time!
Link: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2309.01586.pdf
Cybercriminals Use Generative AI (…) to Run Their Scams
Speaking of baiting scammers – I wonder if somewhere on the Internet right now the LLM-defender is baiting the LLM-scammer.
Link: https://abnormalsecurity.com/blog/generative-ai-nigerian-prince-scams
Regulations
Dallas AI newsletter on AI regulations in various countries

Link: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/state-ai-regulation-september-2023-newsletter-dallas-ai/
Overview of the AI regulations in various countries from Reuters
Link: https://www.reuters.com/technology/governments-race-regulate-ai-tools-2023-09-13/
If you want more papers and articles
To be honest, I just took a look at the abstracts of those papers below due to the lack of time, but maybe you will find some of them interesting.
“Software Testing with Large Language Model: Survey, Landscape, and Vision” – Wang, et. al.
Link: https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.07221
“MathAttack: Attacking Large Language Models Towards Math Solving Ability” – Zhou, et. al.
(This one is interesting, take a look at those examples:

)
Link: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2309.01686.pdf
“INTEGRATED PHOTONIC AI ACCELERATORS UNDER HARDWARE SECURITY ATTACKS: IMPACTS AND COUNTERMEASURES” – de Magalhaes, Nicolescu, Nikdast
This paper is on hardware trojans in the silicon photonic systems. Probably you need to have some advanced knowledge (which I don’t have) to be able read it, but when I saw this title, I felt like in this meme, so I am just sharing the link:

Link: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2309.02543.pdf
Remember that you can subscribe this newsletter here: https://hackstery.com/newsletter
If you find this newsletter useful, I’d be grateful if you’d share it with your tech circles, thanks in advance!